Why factors should be promoting JLM DPF Cleaner

DPF cleaning products are in a hotly contested category. Knowing which one to promote to your trade customers, especially, is challenging because not all DPF additives are the same, according to Kalimex Managing Director, Mike Schlup.
There are big differences, depending on the type of catalyst used as the base ingredient. Ferrocene, or iron, is a commonly used catalyst, which assists particle burn by artificially increasing the temperature in the DPF. Although achieving the overall aim of reducing the particulate load in the filter, the downside is that the elevated temperatures of up to 800°C risk irreversible damage to the DPF core, particularly with overuse of this type of additive.
Iron-based catalysts also result in increased levels of ash deposits, and these can only be removed with an off vehicle physical clean of the DPF.
I believe the safer alternative to iron-based formulas is cerium and platinum, as found in the JLM DPF Cleaner fuel additive, for example. Each element plays a unique role in catalysing chemical reactions within the DPF, ultimately leading to more efficient combustion of soot particles and improved filter performance.
Here’s how each ingredient works:
Cerium oxide is a versatile catalyst because it possesses excellent oxygen storage and release properties, allowing it to facilitate the oxidation of soot particles at lower temperatures. Cerium acts as a promoter, accelerating the combustion of trapped soot within the DPF during regeneration cycles.
Platinum is a precious metal with remarkable catalytic activity, particularly in promoting the oxidation of hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide. When combined with cerium, platinum enhances the overall effectiveness of the catalyst system by further lowering the ignition temperature of soot particles and improving their combustion efficiency.
How cerium and platinum perform together:
Soot combustion: The combination of cerium and platinum in a fuel additive enhances the combustion of soot particles within the DPF. Cerium facilitates the initial oxidation of soot at lower temperatures, while platinum provides additional catalytic activity, ensuring thorough combustion across a broader temperature range. This synergistic effect results in more complete soot removal and reduced DPF blockages.
Ash reduction: In addition to promoting soot combustion, cerium and platinum help minimise ash accumulation within the DPF. By facilitating the conversion of ash into less harmful forms during regeneration, these additives contribute to maintaining DPF efficiency and prolonging its lifespan.
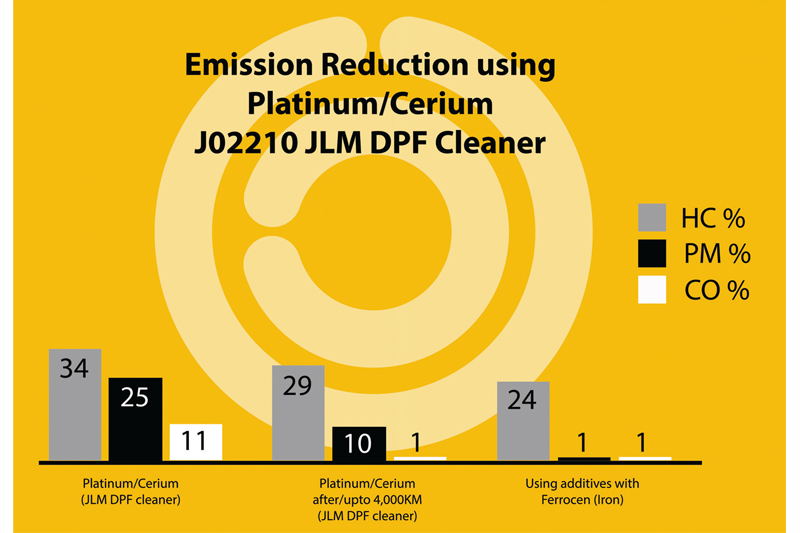
In short, the cerium-platinum combination offers outstanding catalytic activity, particularly at lower temperatures, making it a highly-effective and safe option for maintaining clean and efficient diesel emissions systems. The JLM DPF Cleaner combines cerium and platinum and is more effective than cerium on its own (Fig 1).
It is important to recommend effective and safe additives to your workshop customers, in order to avoid unwanted damage to expensive exhaust components, especially the DPF.








